Designing of solar stations
Building a solar park starts with design!
The aim of the project is to ensure maximum productivity from the investment in the solar power plant. In order for the solution to be long-lasting and to maximize the return on money, the foundations and construction of the plant must be well-thought-out from the very beginning, and the fastening devices must be purchased from certified manufacturers. Only on the basis of a correctly designed solution is it possible to clearly indicate the investment for the construction of the plant, the payback period and to guarantee the long-term guaranteed cash flow productivity of the plant. Imagine that you are building a house with no drawings and stones are just being laid – acting this way and assuming that the solution will be good is not sensible!


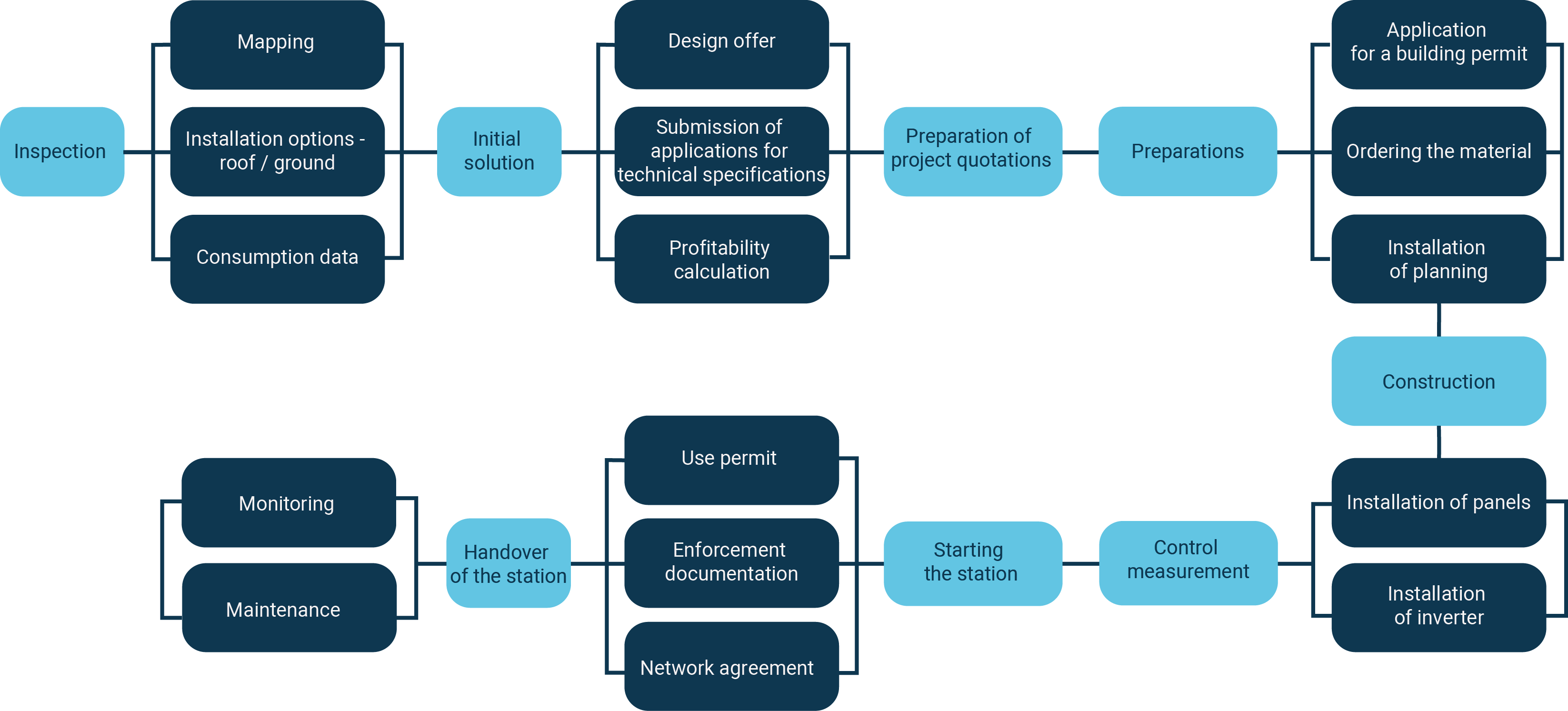
The design begins with a thorough inspection, during which the main aspects of the design are identified.
- Mapping how large, reasonable and optimal a solar power plant is possible to design/build considering the company’s energy consumption profile.
- Roof covering material, roof slope, direction to weather maps, estimated load capacity.
- It will be determined whether it is more optimal to install the station on the roof or on the ground.
- Possible connection of the station either directly to a large consumer/device (e.g. refrigeration unit) or to the main panel of a building.
- Possible installation location of the inverter.
- The passage of cable routes and the entry of the power cable into the building.
The solar power plant project determines:
- the location of the station on the territory and in relation to the weather maps
- power of the station
- connection to the building’s electrical and automation system
- the maximum and optimal number of panels to be installed
- installation features
- the number of panels in one circuit
- the mounting solution used
- production forecast
Based on the project, it is possible to apply for a building permit and a later use permit from the local government. After receiving the use permit, a completed form must be sent to Elektrilevi to receive renewable energy support.


Parts of the project
- Explanatory memorandum
- Position plan
- Structure diagram of the main shield
- Solar switchboard
- Wiring diagram of the panels
- Monitoring system
- Communication solution
- Voltage drop calculation
- Inverter connection diagram
- Newsletters
- Maintenance requirements and instructions
- Economic calculation
Design process of a solar station
Schedule the design process
Stage |
Time |
| Site inspection and information gathering | 1. week |
| Pre-presentation of the project | 2. week |
| Project preparation | 2. – 3. week |
| Issuance of technical conditions of Elektrilevi | up to 60 days |
| Preparation of solutions and offers | 4. week |
| Presentation of the project to the client | 5. week |

What are the main design and construction errors?
| Problem | Impact |
| AC power cables are underdimensioned | Fire hazard, voltage drop, decreased income |
| The formation of shadows is not taken into account (trees, chimneys, ventilation hatches, roof edge, etc.) | Lower productivity, non-productive circuits |
| Too few inverter circuits | Lower productivity and financial loss |
| Too few panels or the distribution of panels in the chain is incorrect | Lower productivity, financial losses and the station will be operational significantly later |
| Low quality manufacturer’s panels | Lower productivity, shorter service life, shorter production cycle, risk of fire |
| The solar station does not need maintenance – WRONG! | Fire hazard, lower productivity, risk of plant destruction |
| Incorrect installation of inverters | Lower efficiency and additional cooling required |
| Wrong inverter selection | Loss of production, low response speed, no after-sales service, solving problems is time and money consuming |
| Incorrect calculation of wind load | Panels fly off the roof, roof damage, dangerous to people |
| Incorrectly selected protection devices | Protection is applied too early, risk of fire |
| Wrong cable selection | Investment under- or over-dimensioned, installation complexity, risk of circuit breakage, cable damage |
| Wrong mounting angle | Panels fly off the roof, roof damage, dangerous to people, low productivity |
| Wrong choice of mounting and fastening accessories | The panels fly off the roof, the roof is damaged, the roof starts to run through |
| Non-use of cable trays | Risk of mechanical damage to cables, risk of short circuit, dangerous maintenance |