Energy audit of a large enterprise
The Ministry of Economic Affairs and Communications has adopted the Energy Sector Organization Act, which obliges large enterprises to conduct regular energy audits. Large enterprises must undertake an energy audit of the company every four years by the time-limit provided in the Act, i.e. six months after the Act enters into force (05.12.2019). The obligation to perform an energy audit in a large enterprise is based on Article 8 of the European Union Energy Efficiency Directive 2012/27/EU, and according to the Ministry, Estonia must transpose this directive.
Free consultation

What is a large enterprise?
According to ENMAK, large undertakings are those companies with more than 250 employees and a company’s balance sheet total of more than € 43 million and/or sales revenue of more than € 50 million (parent company or consolidated, including international groups and owners in other countries). There are almost 300 such companies in Estonia. An energy audit of a large company must be performed regardless of the company’s field of activity or the amount of energy consumption. In the case of a statutory audit, both the parent company and its related companies under the control of the parent company are audited. However, the audit obligation is determined based on the criteria of the parent company. In energy audits performed for international companies, only the energy use of parts of the company located in Estonia is audited.
An undertaking has the right to prove that it is not a large enterprise if there are grounds for doing so by submitting the necessary documents (last annual report) if the state supervises this obligation.
There are two ways to meet the requirement:
-
Carry out an energy audit every four years, which meets the conditions of Regulation 76 and is carried out by an auditor/specialist with the necessary qualifications.
-
Implement an environmental or energy management system in the company that meets the requirements of Standard 1 ISO 50001, Standard 2 Standard ISO 14001 or European Union EMAS Regulation 3.
To meet the requirements of the energy audit, the enterprise must have a valid management system certificate (valid for EMAS registration) issued by an independent and duly accredited organization. The management system must also cover the minimum requirements set out in Regulation 76.
How to meet the requirement?
Who can undertake an energy audit?
The competence of the lead auditor is determined by the energy consumption of the buildings, the installed cooling capacity and the installed capacity of the local heat source. DeltaE recommends ordering an energy audit from a company that holds at least a Level 7 of energy performance specialist (assumes that the total energy consumption does not exceed 5 GWh or the installed thermal capacity does not exceed 1 MW). If these indicators are exceeded, a Level 8 energy performance specialist is required to be an auditor. The involvement of a higher level specialist will certainly ensure better results and more extensive work.
- In the course of collecting source data for an energy audit, the following shall be mapped on a monthly basis for at least one year and, if possible, for a longer period of time: 1) energy use for electricity, heat, gas, liquid fuel and solid fuel; 2) energy production in respect of different types of energy; 3) renewable energy production and its use.
- In the course of the energy audit analysis: 1) an energy balance is compiled by different types of energy of the enterprise; 2) an assessment is made of the current state of energy use and production; 3) a baseline scenario for the use and production of energy is determined, which expresses the situation if no efficiency measures are implemented; 4) alternative development scenarios for energy use and production are determined; 5) an assessment of the energy saving potential of development scenarios for energy use and production is performed; 6) a comparison between the development scenarios of energy use and production is performed, as a result of which the priority and expediency of these scenarios are determined.
- In assessing the energy saving potential of the development scenario of alternative energy use and production, the following shall be determined for the development scenario of energy use and production: 1) the activities and measures necessary for the implementation; 2) the estimated cost of implementation; 3) estimated energy savings; 4) estimated reduction in carbon dioxide; 5) the estimated impact on the income and expenses of a large enterprise; 6) economic profitability; 7) risks and dangers; 8) feasibility analysis and recommendations for implementation.
NB! Energy audits do not map anything technically and the solutions developed are general. The costs and savings of the final recommendations are approximate. In order to reach real solutions, a team of specialists must be involved and an audit of energy saving solutions must be prepared.
What does an audit consist of?
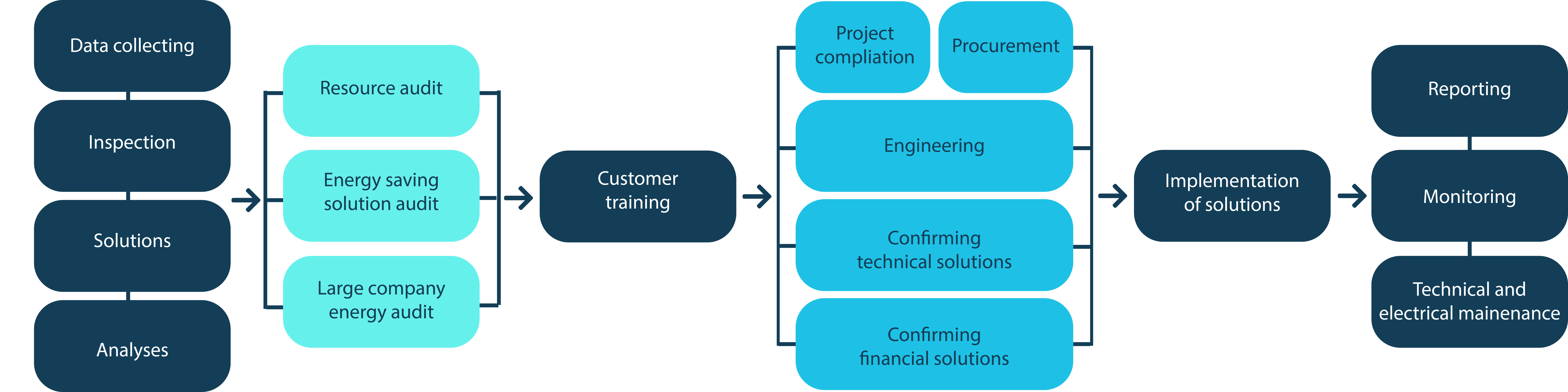
The whole process of implementing energy saving solutions
Schedule of the usual audit process
Stage |
Timeline |
| Signing a contract | 1. week |
| Collecting source data | 1. -2. week |
| Conducting inspections | 3. week |
| Carrying out measurements | 3. – 4. week |
| Preparation of the audit report | 4. – 5. week |
| Presentation | 6. week |
| Implementation of solutions | 7. week |

What does DeltaE Engineering offer?
The goal of DeltaE Engineering Office is to offer a complete solution and prepare an audit according to the client’s needs, which meets all goals! A full audit consists of two parts, where the energy audit ensures compliance and the audit of energy saving solutions develops technical solutions. Our responsibility is to produce a world-class audit, ranging from resource efficiency to energy solutions. Energy audits alone do not create any technical solution or ensure savings! This requires investment.
DeltaE Engineering vs. consulting company
| Our capability | Consultation company | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Standard audit | ||
| 2. Design ability and experience | ||
| 3. Preparation of an energy saving solutions audit | ||
| 4. Experience in installing and implementing technical solutions | ||
| 5. The most competent and broad-based team | ||
| 6. Involvement of equipment and performance of basic measurements | ||
| 7. Possibilities for additional analyzes and measurements | ||
| 8. Solutions for monitoring and surveillance systems | ||
| 9. Monitoring, maintenance and electrical operation | ||
| 10. Financing solutions | ||
Energy audits prepared by DeltaE and Energex

Merinvest OÜ
- Field industry
- Audit completion date 2019
- Number of buildings 9
- Number of measures 7
- Volume of audit 55 pp

Scanfil OÜ
- Field industry
- Audit completion date 2019
- Number of buildings 3
- Number of measures 5
- Volume of audit 53

SA Põhja-Eesti Regionaalhaigla
- Field health care
- Audit completion date 2019
- Number of buildings 8
- Number of measures 19
- Volume of audit 116 pp

SA Tartu Ülikooli Kliinikum
- Field health care
- Audit completion date 2019
- Number of buildings 7
- Number of measures 15
- Volume of audit 107 pp

VKG OIL AS
- Field industry
- Audit completion date 2018
- Number of buildings 6
- Number of measures 9
- Volume of audit 83 pp

Enics Eesti AS
- Field industry
- Audit completion date 2019
- Number of buildings 2
- Number of measures 6
- Volume of audit 65 pp

ELME Metall OÜ
- Field industry
- Audit completion date 2020
- Number of buildings 4
- Number of measures 5
- Volume of audit 51 pp

Kulinaaria OÜ
- Field industry
- Audit completion date 2019
- Number of buildings 1
- Number of measures 6
- Volume of audit 65 pp

Eesti Post AS
- Field logistics
- Audit completion date 2019
- Number of buildings 17
- Number of measures 13
- Volume of audit 163 pp

Coop Pank AS
- Field banking
- Audit completion date 2019
- Number of buildings 1
- Number of measures 5
- Volume of audit 55 pp

Olerex AS
- Field retail sale
- Audit completion date 2020
- Number of buildings 4
- Number of measures 4
- Volume of audit 55 pp

Ida-Tallinna Keskhaigla
- Field health care
- Audit completion date 2020
- Number of buildings 5
- Number of measures 12
- Volume of audit 115 pp

Eesti Pagar AS
- Field industry
- Audit completion date 2020
- Number of buildings 2
- Number of measures 7
- Volume of audit 60 pp

Harju Elekter AS
- Field industry
- Audit completion date 2020
- Number of buildings 1
- Number of measures 13
- Volume of audit 115 pp

Tallinna Linnatranspordi AS
- Field logistics
- Audit completion date 2020
- Number of buildings 12
- Number of measures 3
- Volume of audit 78 pp

ABC Supermarkets
- Field retail sale
- Audit completion date 2020
- Number of buildings 20
- Number of measures 6
- Volume of audit 62 pp

Amserv Grupi AS
- Field retail sale
- Audit completion date 2020
- Number of buildings 10
- Number of measures 17
- Volume of audit 109 pp

Postimees Grupp AS
- Field media
- Audit completion date 2020
- Number of buildings 8
- Number of measures 7
- Volume of audit 99 pp

ERGO Insurance SE
- Field insurance
- Audit completion date 2020
- Number of buildings 15
- Number of measures 5
- Volume of audit 101 pp

DBT AS
- Field logistics
- Audit completion date 2020
- Number of buildings 5
- Number of measures 5
- Volume of audit 69 pp